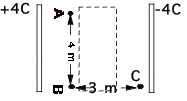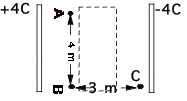Phy 214
Test 2 7
points each 2pts Absolutely free!
Spring
2007
1. Connect
each of these circuits. Make sure
you have
completely discharged the capacitor before each trial.
a.
Give the time it takes for the bulb to go out for each
circuit.
b.
Explain these results.
2.
What happens to the capacitance of a capacitor when :
a.
The size of the plates is doubled?
b.
The distance between the plates is doubled ?
c.
A dielectric with dielectric constant 4 is placed between the
plates ?
3.
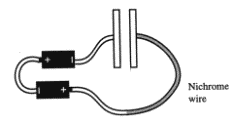
Here is a circuit consisting of two
flashlight batteries, a large air-gap capacitor, a nichrome wire, and
thick copper wires. The circuit is allowed to run long enough that
the capacitor is fully charged with +Q and -Q on the plates.
Next you pull the two plates
further apart. Which way do electrons flow?
Eexplain why in terms of the fundamental concepts of charge
and field (do not use "potential" or "capacitance"). Include
diagrams.
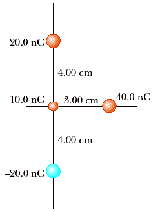
4. Two particles, with charges
of 20.0 nC and -20.0 nC, are placed at the points with coordinates
(0, 4.00 cm) and (0, -4.00 cm), as shown in the figure below. A
particle with charge 10.0 nC is located at the origin. (a) Find the
electric potential energy of the configuration of the three fixed
charges. (b) A fourth particle, with a mass of
2.00 x 10-13 kg and
a
charge of 40.0 nC, is released from rest at the point (3.00 cm, 0).
Find its speed after it has moved freely to a very large distance
away.
5.
If the charge
on each plate is 4 C , the distance between the plates is 6 m, and
the area of each plate is 6 m2:
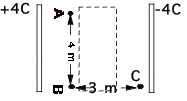
a.
What is the capacitance of this capacitor?
b.
What is the potential difference between the plates?
c. What will the potential
difference between the plates be after a 2m thick piece of metal is
centered between the two plates (represented by the dotted rectangle
)?
d.
5 pts Bonus! What
will be the potential difference between the plates if the piece of metal is replaced by a
piece of plastic whose dielectric constant is 5?
6.
a. What is DVBC
= VC-VBin the figure below?
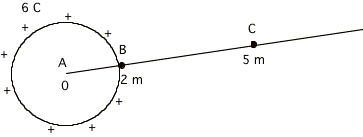
b.
What is the work required to move a -2 C charge from B to C in
this figure?
c. The
voltage V at C is actually the change in
voltage DV from where to C ?
d.
What is DVAC
?
7.
Rank these bulbs in order of
brightness from highest to least .
All bulbs are identical.
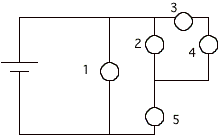
8. Find
the
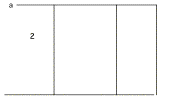
total capacitance between a and b.
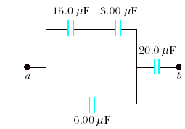
9.
Fnd the total resistance between a and b.
10.
The resistance of a platinum wire is to be calibrated for
low-temperature measurements. A platinum wire with resistance 1.00 ˝
at 20.0ĄC is immersed in liquid nitrogen at 77 K (-196ĄC).
If the temperature response of the platinum wire is linear, what is
the expected resistance of the platinum wire at -196ĄC?
(a for platinum = 3.92 x 10-3/ĄC)
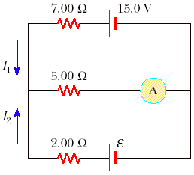
11.
The ammeter shown in Figure below reads 2.00 A. Find the
system of equations that determine I1, I2, and e.
 12. The quantity of
charge q (in coulombs) that has passed through a surface of area 2.00
cm2 varies with time according to the equation q =
4t3 + 5t + 6, where t is in seconds.
What is the instantaneous current through the surface at t =
1.00 s?
12. The quantity of
charge q (in coulombs) that has passed through a surface of area 2.00
cm2 varies with time according to the equation q =
4t3 + 5t + 6, where t is in seconds.
What is the instantaneous current through the surface at t =
1.00 s?
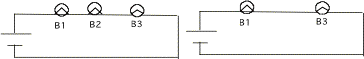
13. Bulbs
are identical in mechanical
construction. The steady state
electron current with three bulbs in the circuit is 3x
1017 electrons / sec. Next,
the middle bulb,
B2 is removed and replaced by a wire.
Now what is the electron current in the circuit .
Show your work.
<![if
!supportEmptyParas]> <![endif]>
14.
When a round bulb and long bulb are connected in series, the
long bulb lights and the round bulb does not.
Explain why.