Phy 214 Test 1 8 pts each Feb. 2, 2007
(4 pts Absolutely FREE!)
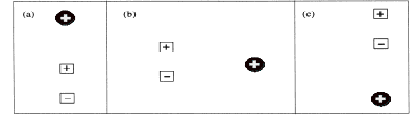
1. In each diagram below, draw a vector showing
each force vector and the net force on the round particle due to all the square
fixed charges. Make sure all
vectors are drawn to lengths indicating relative magnitudes of forces.
![]()
2.
A large positive charge pulls on a distant electron. How does the net force on the electron change when a slab of glass is placed between
the large positive charge and the electron ? Explain using ONLY carefully labeled diagrams. (Be sure to show ALL the forces on the
electron before determining the net force on the electron.)
3.
a. In the diagram, a rubber
rod is given a charge Q distributed uniformly over it by rubbing it with fur. It is noticed that when an uncharged
metal ball is suspended
by a string at a particular location near the end of the rod is drawn toward
the rod by some mysterious force.
Show the distribution of charges on both the rod and the ball and
explain why this occurs.

3 b.
When the rubber rod is removed, and replaced by a metal rod of the same
length which has been given the same amount of charge, it is found to cause the
ball to come much closer.
Show the distribution of charges on both the rod and the ball and
explain why this occurs.

4.
These two solid spheres initially have
the charge evenly distributed on their surfaces. Find magnitude and direction of the electric field at the points A, B, and C .
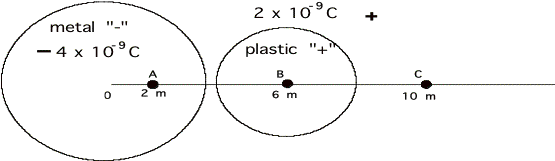
5.
Many people believe current output by a battery is fixed.
a.
Describe (or draw ) two different circuits in which the same battery
produces two different amounts of current.
b.
Explain how you know the current is different in the two circuits.
6.
A single wire across the top of the compass causes a deflection of 30¡
in needle. If it is now curved
back along side the first wire, the needle will now have what deflection?

7. The charges in the
diagram below are located on the corners of a square that is 6 m on each
side. Find the magnitude and
direction of the electric field at P. (Hint # 1: There is a really hard way to do this problem and there is
a really really easy way to do it.
) (Hint # 2: Well now, tests are
supposed to be learning experiences.
This problem is a test to see whether or not you learned anything from
the experience of doing problem 1.)
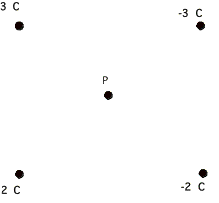
8.
What you see in the figure below is a cut-away view of a hollow metal
sphere. The gray area indicates solid metal. The white region in the center
indicates the hollow center, at the center of which has been placed, some
magical how, an unknown charge Q3.
We have been able to detect a 20 C charge Q2 on the inside
surface of the shell, and also that the electric field is 1.8 x 109
N/C at a distance of 5 m from the center of the system, we need your assistance
to determine what charge Q3 is located at the center, and how much
charge Q1 is on the outer surface of the sphere.
Thank you for your help, we have every
confidence that you can solve this problem and save our mission!
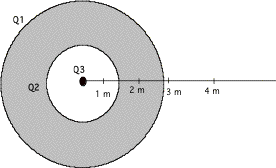
9.
Where would you place an electron ( charge is 1.6x10-19C.) so
that the electric field at P would be 300N/C to the left.
![]()
10.
Consider a thin plastic rod. The rod carries a
uniformly distributed positive charge Q. Follow the steps below to obtain the components Ex and Ey
of the electric field at the origin, due to the rod.
a)
Use a diagram to explain how you plan to cut up the charged rod, and
draw the DE contributed by a representative piece.
b)
Express algebraically the contribution each piece makes to the x and y
components of the electric field .
Be sure to show your incremental component dE of the electric field on
your drawing. (Recall that the arc
length Ds of a circular arc of radius R ,
subtended by an angle of Du, is R Du.)
c)
Write the summation as an integral for each component of E, and simplify
the integral as much as possible.
State explicitly what the range of your integration variable is.
d) 5 points Bonus! Evaluate the
integrals to find Ex and Ey.
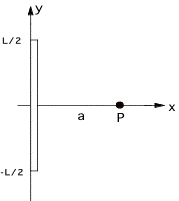
11. Here is a view from above of a
portion of a circuit containing three identical light bulbs (the rest of the
circuit including the batteries is not shown).
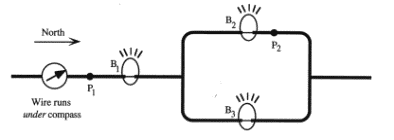
(a) The compass is placed on top of the wire, and it deflects 20 degrees
away from north as shown (the wire is underneath the compass). What direction are the
electrons moving at location Pl ? How do you know?
b) In the steady state, 3 x 108
electrons pass location Pl every second. How many electrons pass location P2
every second? Explain briefly.
(e) Describe the relative brightness of
bulbs Bl, B2, and B3. Explain briefly.
12.
a. Connect the circuit
below.
b.
then measure and record the deflection angle in each of the boxes.
c.
circle the correct response.
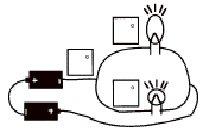
a.
These two bulbs have the same brightness
b.
The long bulb is brighter than the round bulb.
c.
These two bulbs have the same current flowing through them.
d.
The electric fields in the two bulb filiments are the same.
5 Pts Bonus each!
B1.
If current flow is inversely proportional to length of wire, (you can
think of two bulbs as one bulb with twice the length), why doesn't the current
drop in half when a second identical bulb is placed in series ?
B2. On a clear and carefully drawn diagram, place a zorac
nucleus and an electron
in such a way that the
electric field due to these charges is zero at a location marked x. (A zorac
nucleus contains three protons and three neutrons.) Explain briefly but
carefully, and use diagrams to help in the explanation. Be quantitative about
the relative distances (That means
give a formula for one distance in terms of the other, or give an algebraic
expression for the ratio of the two).